Introduction.
Stem cells are often called the body’s master cells because they have the unique ability to transform into many different types of cells. (develop into other cell types such as nerve cells, muscle cells, or blood cells). Unlike normal cells, stem cells can self-renew (make copies of themselves).
In medicine, stem cells are considered an important tool for treating diseases, repairing damaged tissue, and even regenerating any part of the body. Scientists and doctors believe that stem cell-based therapies will play an important role in future healthcare.
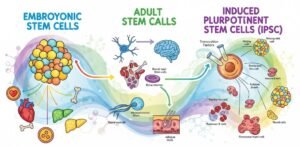
Types of Stem Cell.
Embryonic Stem Cells.
They are the pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocysts.
- Derived from early-stage embryos.
- Pluripotent cells can develop into nearly all cell types in the human body.
- Highly powerful but raise ethical concerns since they come from embryos.
Adult Stem Cells.
They are the undifferentiated cells found in specific tissues of the body after development.
- These are found in bone marrow, skin, blood, and liver tissue.
- These are widely used in bone marrow transplants for blood cancers.
- These are usually used in abundance and can develop into a limited number of cell types.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.
- It is created in the lab by reprogramming adult cells back to a pluripotent state.
- Embryonic stem cells can function similarly but avoid ethical issues.
- Stem cell research has been revolutionized since its discovery in 2006.
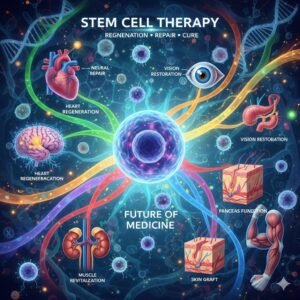
Role of Stem Cells in Medicine.
Stem cells are unique because they can self-renew. These properties are very helpful in disease diagnosis and treatment.
Tissue Regeneration Medicine.
- Stem cells repair the cells and tissues damaged by disease or injury.
- Stem cells are used to regenerate the heart tissue after a heart attack.
Organ and Tissue Replacement,
- Scientists use stem cells to enlarge small organs.
- Scientists are using lab-grown livers, kidneys, and even hearts for future transplantation use.
Neurological Disease.
- Stem cell therapy is being tested for a variety of neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries.
- They play an important role in replacing damaged neurons and restoring brain function.
Immune System and Blood Disease.
- Bone marrow contains hematopoietic stem cells that are used to treat leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell anemia through bone marrow transplants.
Diabetes Tretment.
- Scientists are developing stem cell-based therapies to create insulin-producing beta cells for patients with type 1 diabetes.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy.
Stem cell therapy is the most beneficial in modern medicine. It is used to naturally repair tissue and heal injuries, and restore damaged tissue. This therapy is long-lasting. One of the advantages of stem cells is in treating degenerative diseases including but not limited to Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, where it assists with the regeneration of nerve cells and is improving neurological function generally. Stem cells also work to treat orthopedic problems such as joint injuries, osteoarthritis, joint disease, and spinal cord damage through tissue and cartilage regeneration. Finally, stem cell therapy appears to have great promise in treatment heart disease, particularly in helping to regenerate damaged heart muscle from a heart attack.
- They regenerate tissue by naturally healing.
- They reduce the dependence on the donor organ.
- The patient’s stem cells are used in their personalized medicine.
- They are the hope for those diseases which is untreatable.
Future of Stem Cell in Medicine.
They will not only integrate with modern biotechnology, but they will change medicine by offering remedies for chronic diseases.
- 3D printing technology will be used with stem cells to create functional tissues.
- Gene editing and stem cells will correct genetic disorders at the cellular level.
- The patient‘s stem cells are removed so that they can form an organ the body will not reject.
- Broaden Clinical Trials: Additional clinical trials will begin testing stem cell treatments in more diseases
Conclusion:
Stem cells are a part of the future of medicine, representing a new hope for millions of patients around the globe. The potential outcomes stem cell therapy will yield, from blood cancers to damaged organs, are limitless. Despite the hurdles that lay ahead: ethics, cost, safety, the future of stem cell therapy looks bright. Stem cells will not only heal diseases in the future, but redefine how we think about healing and the state of being human.