Golgi Apparatus.
The cells are the basic units of all living organisms, and they have many tiny structures in the cytoplasm called organelles. They carry out important reactions for survival. The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a vital organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was discovered by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi in 1898 and is named after him.
The Golgi apparatus functions as the cell’s packaging and distribution center. It plays a key role in processing and modifying proteins and lipids that are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Once processed, these molecules are packaged into vesicles and sent to their proper destinations inside or outside the cell.
Discovery.
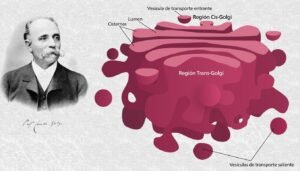
In 1898, Camillio golgi, a scientist, first discovered the Golgi Apparatus when he studied the nerve cell under a light microscope. At that time, the microscope was not as advanced, and many scientists did not accept this discovery due to an optical illusion. In the 20th century, advances in electron microscopes created then scientists to confirm the Golgi apparatus existance. He got the Nobel Prize in 1906, in Physiology or Medicine. This is an important organelle in the scientific history.
Structure.

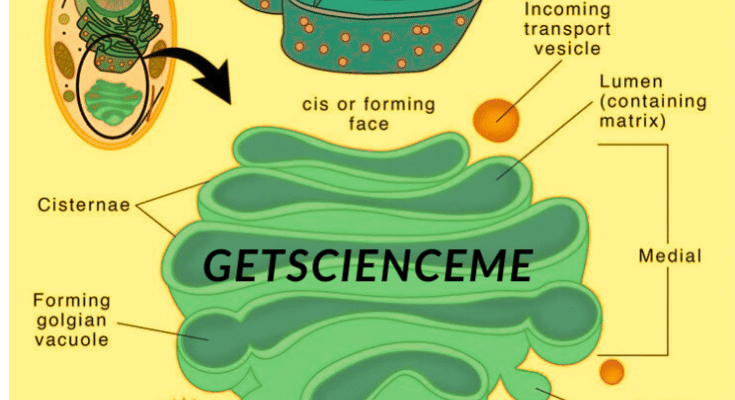
They are the membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm near the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) and the nucleus. The structure is very highly specialized and consists of flattened, membrane-bound sacs called Cisternae. They are arranged in a series, like a set of bundles.
- Consiste of stacked flattened, membrane-bound sacs (cisterne)
- Cis face ( forming face) receives protein and lipids from the Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- Trans face ( maturing face), they dispatch processed molecules in vesicles.
They ensure the movement of the molecules in an organized manner. Molecules start from the Cis Face and move toward the Trans Face.
Functions.
The Golgi Apparatus, also known as the “Post Office of the Cell,” because its main function in the processing, packaging, and transport of molecules.
Protein Processing:
Protein is synthesized on the endoplasmic reticulum, and they transported to the Golgi apparatus, where many modifications are made and form a glycoprotein by the addition of carbohydrates to the protein group. and also occurs Phosphorylation, and the other is the Sulfation addition of the sulfate group. These modifications are very important for the final function of the protein
- Modifies the protein received from the Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- Adds carbohydrate to form glycoproteins.
Lipid Processing:
Another function of the Golgi Apparatus is to modify and transport lipids. When lipid molecules like glycolipids are synthesized, they are packed and transported or delivered to the plasma membrane or organelles. The Golgi apparatus not just delivers glycolipids, it also other lipids molecules synthesized and transport, such as sphingolipids and cholesterol. The sphingolipid synthesis process starts from the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic Reticulum synthesizes basic sphingolipids called Ceramide. Ceramide transport to the Golgi apparatus. It is further modified by the Golgi apparatus and forms sphingomyelin. When sugar is added, then Glycosphingolipids are formed.
Packaging & Transport:
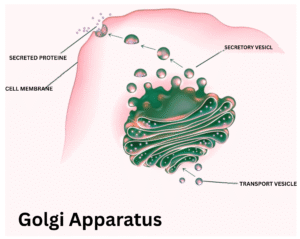
The Golgi apparatus packages the proteins and lipids into the Golgi vesicles, which are the tiny structures that deliver the
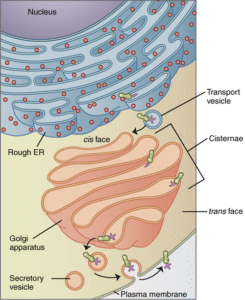
molecules into the different parts of the cells. Some vesicles transport molecules to the plasma membrane, and others transport enzymes to the lysosomes. The Golgi apparatus is the central hub of the vesicles.
- They pack materials into vesicles.
- Directs them to the lysosome, plasma membrane, or secretion.
Formation of Organelles:
Lysosomes are the tiny organelles which formed by the Golgi apparatus. They are the membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. The main function of the lysosome is to break down the waste material of the cells and maintain the cell.
- Plays a role in lysosome formation.
- Help with acrosome formation in sperm.
Secretion:
In some specialized cells secreted the hormone. The Golgi apparatus plays a major role in the release of hormones and other substances. In the Pancreas, pancreatic cells release insulin, the Golgi apparatus packages the insulin in vesicles, and then secretes it into the blood vessels.
- Produce secretory vesicales.
- Important for hormone and enzyme release.
Role.
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi body, plays an important role in eukaryotic cells. It transports the newly synthesized protein and lipids. The Golgi apparatus also produces lysosomes, consisting of enzymes to break down waste products in the cell, and in plant cells, it aids in the synthesis of materials that form the cell wall. The Golgi apparatus acts as the “post office” of the cell by modifying the molecules and then delivering those molecules; thus making the Golgi apparatus an important component to overall cell growth, communication, and function.
The Golgi apparatus also plays an important role in the cell for communication between cells. The protein and lipids act as the signalling molecules, such as hormones or neurotransmitters. Without the Golgi apparatus, cells do not coordinate their complex activity.
Key Facts.
- Modifying proteins (e.g., glycosylation)
- Sorting and packaging proteins and lipids
- Forming lysosomes
- Transporting cellular products
The Golgi apparatus is essential for maintaining cellular function and communication, especially in cells involved in secretion, like glandular or nerve cells.