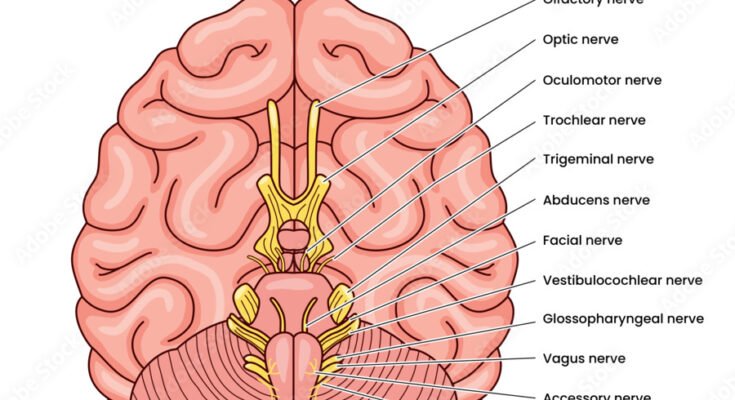
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves that arise from the brainstem rather than the spinal cord (mainly from the brainstem). It is part of the peripheral nervous system(PNS). and play an important role in carrying information between the brain and different parts of the head, neck, and trunk. All nerves do not have the same length; their length depends on the travel in the body. Some are short, some are long. But all originate in the brain/brainstem, and length-wise, their size is different.
The 12 Cranial Nerves ( in order):
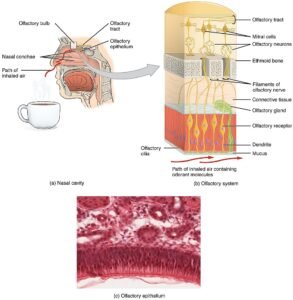
1. Olfactory nerve (I).
The olfactory nerve is the 1st cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve I. It is responsible for the sense of smell. It is the sensory nerve that originates from the olfactory receptor cells, located in the nasal cavity.
- Very short in size, just a few centimeters.
- The main function is smell.
- They reach from the nose to the olfactory bulb.
- Test smell with each nostril while the eyes are closed.
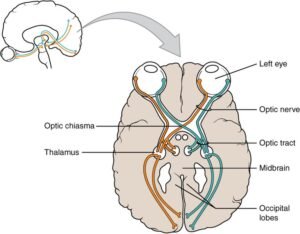
2. Optic nerve (II).
The optic nerve is the 2nd cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve ll. It is responsible for the vision. They transmit visual information from the retina to the eye and send it to the brain for processing and interpretation.
- The length is about 4 to 5 cm.
- The main function is vision.
- They reach from the retina to the optic chiasm.
- Pupil response to light.
- Test visual fields in all 4 quadrants.
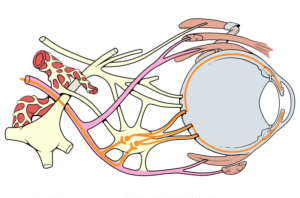
3. Oculomotor nerve (III).
The oculomotor nerve is the 3rd cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve III. It is a mixed cranial nerve. It originates in the midbrain. They mix with predominantly motor functions and some parasympathetic fibers. The early role of the oculomotor nerve is to control the eye’s movements.
- The length is about 2 to 3 cm.
- The main function is eye movement and pupil response.
- They have a short pathway to the eye muscles.
- Pupil response accommodation.
- Check eye movement (up, down, medially).
4. Trochlear nerve (IV).
The trochlear nerve is the 4th cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve IV. It is the smallest cranial nerve that plays an important role in eye movements. It originates in the trochlear nucleus midbrain.
- The length is about 2 to 3 cm.
- The main function is eye movement (downward & inward).
- They go to the superior oblique muscles.
- They assess without head movement.
- Follow an object downward and inward toward the nose for smooth movement.
Generated with AI by pikovit / Adobe Stock
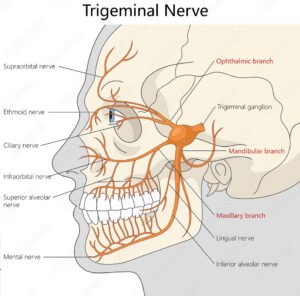
5. Trigeminal nerve (V).
The trigeminal nerve is the 5th cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve V. It is the largest cranial nerve and has both sensory and motor function.. It originates in the pons and divide into the three parts.
- The length is about 6 to 7 cm.
- They are the largest cranial nerves, and their branches go to the face and jaws.
- The main function is sensation and chewing.
- They assess clenching teeth and palpate masseter strength.
- open mouth against resistance.
- Light touch on the forehead, jaw, and cheek.
6. Abducens nerve (VI).
The Abducens nerve is the 6 cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve VI. It plays an important role in controlling eye movements. It originates in the abducens nucleus from the pons and presents to the brainstem.
- The length is about 2 to 3 cm.
- There are short and go to the lateral rectus muscle of the eye.
- The main function is lateral eye movement (side to side).
- They assess to follow an object side to side (without head movement).
7. Facial nerve (VII).
The facial nerve is the 7th cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve VII. It is the mixed cranial nerve with sensory, motor, and parasympathetic. It originates in the pons.
- The length is about 5 to 6 cm.
- They extend to facial muscles and glands.
- The main functions are facial expression and taste.
- They assess raise eyebrows, close eyes, smile, puff cheeks (cheek for asymmetry).
- Taste test on the anterior 2/3 of the tongue (sweet, salty, sour, bitter).
8. Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII).
- The length is about 2 to 3 cm.
- They reach from the inner ear to the brainstem.
- The main function is hearing and balance.
- They assess hearing: Whisper test with ear occlusion.
- Balance: stand with feet together, eyes closed.
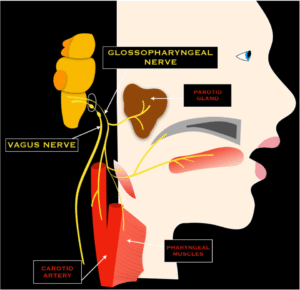
9. Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX).
- The length is about 5 cm.
- They go to the tongue and pharynx.
- The main functions are the gag reflex, swallowing, and taste (posterior of tongue).
- They assess uvula movement.
- Gag reflex test with tongue blade.
10. Vagus nerve (X).
The vagus nerve is the 10th cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve X. It is a mixed cranial nerve with sensory, motor, and parasympathetic. It originates in the medulla oblongata.
- They are the longest cranial nerves.
- The length is up to 30 to 40 cm.
- They extend from the brainstem through the neck, chest, and down to the abdomen.
- The main function is to regulate the rest and digest function & gag reflex.
- They assess the gag reflex, voice quality, and swallowing.
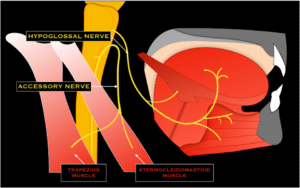
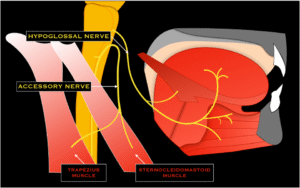
11. Accessory nerve (XI).
- The length is about 6 to 7 cm.
- They go to the neck & shoulder muscles.
- The main function is shoulder shrug & head turn.
- They assess shrug both shoulders against resistance.
- Turn the head on each side against resistance.
12. Hypoglossal nerve (XII).
The hypoglossal nerve is the 12 cranial nerve; they also called the cranial nerve XII. It is the motor nerve that controls the tongue movements. It originates in the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla oblongata.
- The length is about 5 cm.
- They go to the tongue muscles.
- The main function is tongue movement.
- They assess the stick out tongue and move it side to side.